When we think about the origin and who created artificial intelligence, we often think that it is a recent invention, associated with the advancement of personal computers in the 1980s. However, this perception is wrong: the foundations of AI are much older.
The first discussions about AI began in 1940, when Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts presented a pioneering mathematical model of artificial neural networks. At the same time, machines capable of performing complex calculations emerged, such as the machine created by Alan Turing.
From the 1940s to the present day, AI has undergone countless transformations, not only in terms of technical developments, but also in terms of philosophical and cultural reflections on the idea of machines that simulate human reasoning.
Although it is difficult to pinpoint who created artificial intelligence, names such as Alan Turing and John McCarthy (considered the “father of AI”) are fundamental references for consolidating this field of study.
To help you better understand how artificial intelligence came about and who created it, what this technology is, and how it works, we have prepared a comprehensive article. Check it out!
What is artificial intelligence?
To better understand how artificial intelligence came about and who created it, it is worth starting with a clear understanding of what AI is.
In short, AI is a system that processes information in a similar way to the human brain, enabling it to interpret data, recognize patterns, learn from experience, and interact in natural language.
In practice, this means that an AI tool can simulate the way we think, capture messages, analyze them, extract meaning, generate appropriate responses, and even improve over time.
Today, there are tools capable of identifying images and objects, understanding voice commands, suggesting personalized recommendations, and performing tasks autonomously, such as autonomous vehicles, which do not require human intervention in most of the driving process.
Currently, the highlight of AI is generative AI, which gained momentum in 2024. Unlike traditional models, this branch is capable of creating original content, such as text, images, music, and even videos.
To understand this advance, it is essential to know its foundations: machine learning and deep learning, technologies that provide the structure for generative tools to function and evolve.
Maschinelles Lernen
Machine learning consists of training algorithms to identify patterns, make predictions, and make decisions based on data. The main feature of this process is that systems learn through examples, without needing explicit instructions for each task.
Within machine learning, there are several approaches, such as linear and logistic regression, decision trees, random forests, support vector machines (SVM), KNN (k-nearest neighbors), clustering methods, and others.
One of the best-known models is the artificial neural network, inspired by the functioning of the human brain.
It consists of layers of interconnected nodes, which simulate neurons, and has a great capacity to recognize patterns in complex data. For this reason, it is used in areas that require sophisticated analysis of large volumes of information.
Deep Learning
Deep learning is a more advanced branch of machine learning that uses deep neural networks. While traditional networks usually have few layers, deep networks can contain hundreds of them, allowing for much more complex analyses.
This model is capable of unsupervised learning, i.e., identifying patterns and organizing data without relying on human labels. This makes it extremely efficient in applications such as speech recognition, computer vision, and natural language processing.
Generative AI
Generative AI, sometimes called “gen AI,” refers to deep learning models that can create complex original content, such as long text, high-quality images, realistic video or audio, and more, in response to a prompt or user request.
At a high level, generative models encode a simplified representation of their training data and then draw from this representation to create new work that is similar to, but not identical to, the original data.
Who created artificial intelligence?
But who created artificial intelligence? The origin of AI is usually dated to 1943, when Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts developed the first mathematical model inspired by the functioning of neural networks.
Although the term was not yet in use at the time, this study is considered the basis for what would become modern AI. Later, in 1956, John McCarthy was responsible for officially naming the concept with the name we know today.
It is curious to note that, even before there was a name for it, the scientific community was already looking for ways to create artificial systems capable of thinking and learning.
Over time, advances were incorporated, and one of the most notable names in this trajectory is Alan Turing. In 1950, he proposed the famous Turing Test, created to assess whether a system could pass for human in a conversation.
The logic was simple: if the machine could fool the evaluator with its answers, it could be considered “intelligent.”
Although the test was proposed in the middle of the last century, it was not until 2014 that an AI system managed to pass it, by fooling a panel at the University of Reading in the United Kingdom.
This achievement symbolized not only a historic milestone, but also how far the evolution of artificial intelligence has advanced from its conceptual origins to concrete applications.

The emergence of the term artificial intelligence
When discussing who created artificial intelligence, it is impossible not to highlight the year 1956 as a decisive milestone. During this period, the Dartmouth College conference was held in the United States, where the term artificial intelligence was used for the first time by scientist John McCarthy.
The event brought together several researchers interested in discussing the possibility of building machines with human-like abilities. From then on, AI became recognized as a scientific field in the making.
Despite the enthusiasm, there was still a fundamental limitation: the technology of the time did not have sufficient processing power to handle the immense amount of data that such systems would require.
Even so, the topic gained momentum in the popular imagination, driving cultural productions that explored the possibilities of artificial intelligence in creative and often visionary ways.
Technological advances in AI over the years
The real leap forward in artificial intelligence began in the 1990s, when technological advances paved the way for challenges that had previously been unthinkable.
A milestone of this era was the creation of computers designed to compete against humans in strategic competitions, such as the famous chess matches between Garry Kasparov, the Soviet world champion, and systems developed specifically to compete against him.
Kasparov maintained his superiority for a while, but in 1997 the story changed: IBM’s Deep Blue supercomputer managed to defeat him, becoming a symbol of the growing power of machines.
Years later, in 2016, AI surprised everyone again by defeating, for the first time, a world champion of the complex Chinese board game Go. This feat was achieved by AlphaGo, created by DeepMind, a company that is part of Google.
Today, AI is closer to everyday life. With the launch of tools such as ChatGPT and MidJourney, anyone, even without training in technology, can explore the benefits of AI to produce texts, images, or even automate everyday activities.
These resources converse naturally with users and have also become important allies in the corporate environment.
Currently, we are already seeing practical applications in various sectors, such as customer service, with intelligent chatbots that use NLP to provide quick, accurate, and humanized responses.
Examples of AI tools
Today, we already live with different artificial intelligence solutions applied to various everyday tasks. Here are some notable examples:
- ChatGPT
- MidJourney
- Gemini
- DALL-E
Benefits of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence offers significant advantages in a variety of areas and applications. Among the most frequently highlighted benefits are:
Automation of repetitive tasks
AI has the ability to perform routine and repetitive tasks, whether digital or physical, such as sorting products in warehouses and industrial processes.
By taking on these activities, artificial intelligence frees professionals to devote themselves to more creative and strategic functions with greater added value.
Decision support
Whether assisting human decisions or automating them completely, AI enables faster and more accurate analysis, offering decisions based on reliable data.
Combined with automation, it allows companies to seize opportunities and address crises immediately, in real time, without relying on human intervention.
Reduction of human error
AI helps minimize human error by guiding professionals through the correct processes, flagging potential mistakes before they occur, or taking on tasks in a fully automated manner.
This is crucial in sectors such as healthcare, where AI-powered surgical robotics ensure consistent precision. In addition, machine learning algorithms continuously improve their performance by learning from new data and experiences.
24-hour availability and consistency
Artificial intelligence operates without interruption, maintaining stable performance at any time. Tools such as chatbots and virtual assistants reduce the need for customer service personnel, while industrial applications ensure consistent quality and productivity when performing repetitive or complex tasks.
Physical risk reduction
By taking on dangerous tasks, AI protects workers by eliminating the risk of serious injuries or accidents. Autonomous vehicles and other automated systems still in development also offer the potential to increase passenger and operator safety in different contexts.
Impact of AI on society
After learning about who created artificial intelligence, the next step is to reflect on its direct effects on society.
In recent years, we have seen services that already show impressive results, often exceeding the expectations of the general public. Given this, three areas stand out in discussions about the impact of AI.
Changes in the labor market
One of the most recurring debates concerns the replacement of the human workforce by automated systems. Several functions that previously depended on people can now be performed by artificial intelligence with greater speed, accuracy, and efficiency.
A survey released by Gupy shows that, according to PwC estimates, artificial intelligence could generate around 2.7 million new jobs in the United Kingdom by 2037.
The International Labor Organization (ILO), on the other hand, points out in a recent study that only between 2% and 5% of current occupations have a real chance of being replaced by technology, which indicates that the trend is more toward market transformation than mass job losses.
Challenges in the artistic field
Another issue that generates debate is the use of AI to create images, music, and other forms of art. The concern is not limited to the fear that human artists will lose their place, but also to the way these systems were trained: many of them used works by different creators without prior authorization.
In practice, this means that AI can imitate artistic styles without recognizing or compensating their authors, raising ethical and legal dilemmas that still need to be regulated.
Data security and use
For an AI system to work, large volumes of data must be processed. This raises a critical question: who controls this information and how is it used?
Today, personal data protection is one of the most relevant issues globally. Without adequate security measures, there is room for risks such as information leaks, misuse for commercial purposes, or even cybercrime.
Types of Artificial Intelligence
AI applications can be organized into different types according to their capabilities. This classification is not fixed, as the technology continues to evolve rapidly, but three broad categories stand out:
1. Narrow Artificial Intelligence (Narrow AI)
Also called “weak AI,” it is currently the most widely used. It is designed to perform specific tasks and solve well-defined problems. Within it, we have:
- Reactive machines: they do not use memory and respond only to immediate commands. A historical example is IBM’s Deep Blue, which defeated Garry Kasparov at chess in 1997.
- Limited memory machines: they can store information and learn from interactions, enabling simple decisions. This is the case with Netflix’s recommendation algorithms or voice assistants such as Siri and Alexa.
2. General Artificial Intelligence (General AI)
Known as “strong AI,” it is still a concept under development. Unlike narrow AI, it would have the ability to learn autonomously and perform any human cognitive activity, such as reasoning, interpreting contexts, solving new problems, and adapting to different situations. Although it is still in the research phase, it is considered one of the most ambitious goals in the industry.
3. Artificial Superintelligence (ASI)
This type still belongs to the theoretical realm. The idea is that AI with this capability would surpass human intelligence, creating solutions and making decisions in areas involving science, art, or social relations.
This possible advance, however, raises discussions about ethics, security, and human control in the face of increasingly powerful autonomous systems.
Use AI in your customer service
Now that you know more about who created artificial intelligence, we want to introduce you to a tool to optimize and streamline your customer service. JivoChat has an AI tool to optimize customer service across all integrated channels.
With it, you can create automatic responses, even when your team is busy, ensuring that customers receive immediate support.
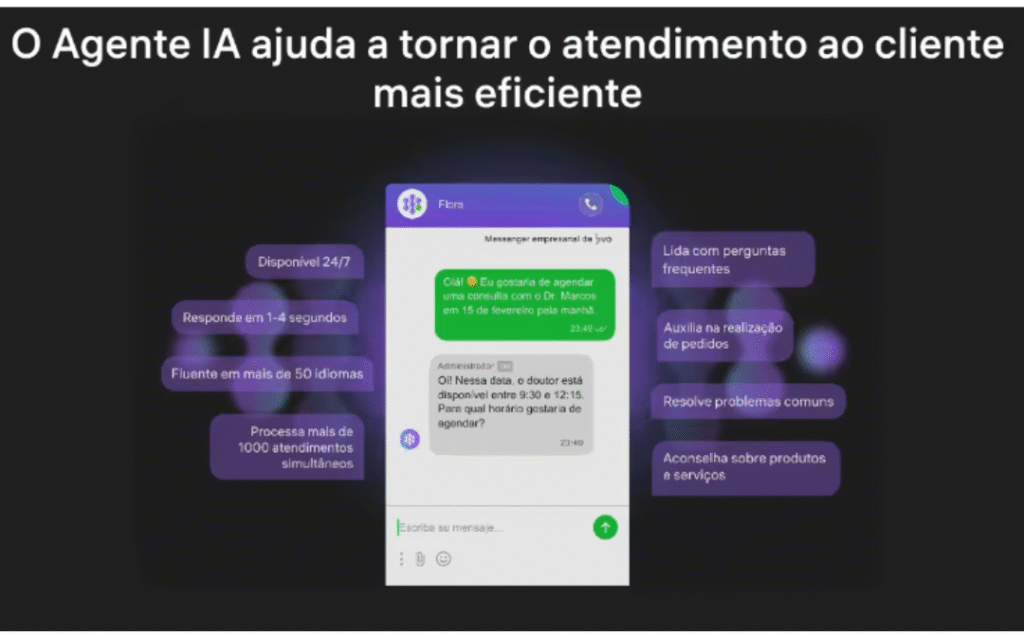
Agents can use quick messages, choose AI-generated suggestions, edit before sending, or send directly without changes, offering greater agility and consistency in customer service.
Key features of JivoChat’s AI Chatbot
Continuous support, 24 hours a day
Multi-language support
Integration with various platforms
Connection to artificial intelligence systems
Generation of programmable codes and scripts
To start using JivoChat’s AI chatbot, check out this complete guide. In it, you will find all the instructions to configure your chatbot and automate customer service, taking full advantage of the benefits of technology to respond quickly to customer requests.